The Problem:
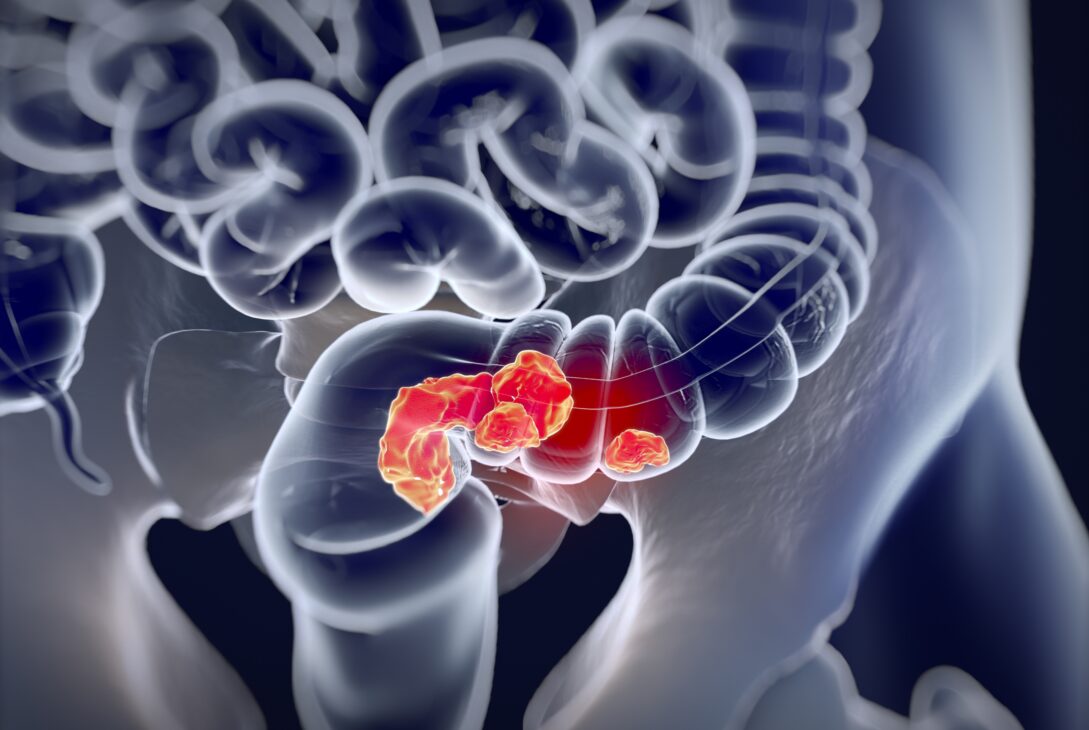
Colorectal Cancer (CRC): It is fourth on the list of life-threatening cancers in the United States and the number of incidents is rising mostly among people under fifty years of age. Currently, there is no accurate non-invasive test to detect nonhereditary colorectal disease for that age group. The blood tests and noninvasive fecal tests currently available lack accuracy.
The Solution:
In a City of Hope study, a blood-based biomarker has been identified that is able to detect early-onset colorectal cancer.
According to a recent article in Inside Precision Medicine, Professor Ajay Goel chair of City of Hope’s Molecular Diagnostics Department commented that the study represents a first in the development of a valid microRNA biomarker that will recognize colorectal cancer in its early stages. The study was recently published in the Gastroenterology journal.
By definition, a microRNA is a small single-stranded non-coding RNA molecule.
It is significant that this microRNA, in detecting early-onset colorectal cancer, will be of benefit to younger patients who are generally diagnosed with late-stage aggressive disease.
About the Study
The researchers used a public database for their analysis to detect miRNA They first stripped away patient data associated with Stage I and Stage II early-onset CRC and also late-onset disease.
Then in order to validate the results they used the blood samples of 149 patients who had early-onset disease. This was compared with a 110-person control group.
After the miRNAs were eliminated, the investigators from the City of Hope identified four miRNAs. These were integrated into an early-onset marker of CRC and a diagnostic, (blood-based), was developed that detects the early onset of CRC.
Looking Forward
Eventually, the test may be used in a physical exam to detect CRC or at six-month intervals in accordance with specific inherited genes that put these individuals in a high-risk category.
The City of Hope, a designated NCI cancer center, takes a state-of-the-art approach in its endeavor to provide cancer care and research to its Southern California patients.
Last modified: April 11, 2023